A healthy and balanced diet is essential for good health and nutrition
If you want to live Healthy Life then you have to eat balanced and Healthy diet containing high nutrients to maintain your good health. A healthy and balanced diet protects against many chronic noncommunicable diseases, such as heart disease, diabetes and cancer. But many of us do not know how they can get all the required nutrients their bodies need.There is no one such particular food item that can provide entire nutrition to our body for optimum functioning, so in order to have a balanced diet we need to have a variety of foods to ensure that we get all the nutrients in optimum quantity. We need different amounts of various nutrients at different stages of life to stay healthy and active.
Study shows that the body needs daily supplement of 40 different nutrients for good health. These nutrients are not available in one type of food. Eating a variety of nutrients rich foods, can supply all the vital nutrients needed for body metabolism. You should include whole grain products in your meals to provide the body with enough energy. Eating a variety of foods and consuming less salt, sugars and saturated and industrially-produced trans-fats, are essential for good health.
 |
| Healthy Diet - Eat a balanced diet to promote good health |
A healthy diet comprises a combination of different foods. These include:
A Healthy Diet for Children- Breastfeeding for babies
- Staples like cereals (wheat, barley, rye, maize or rice) or starchy tubers or roots (potato, yam, taro or cassava).
- Legumes (lentils and beans).
- Fruit and vegetables.
- Foods from animal sources (meat, fish, eggs and milk).
1. Healthy Diet from Birth (Breastfeeding for babies)
A healthy diet starts early in life - breastfeeding fosters healthy growth, and may have longer-term health benefits, like reducing the risk of becoming overweight or obese and developing noncommunicable diseases later in life.
Baby need no other supplemental nutrition other than breast milk for at least the first six months after birth.
what exactly is in breast milk that makes is so good for health?
Proteins :- Whey and casein are the two main types of proteins found in breast milk, about 60% and 40% respectively. These proteins help to regulate digestion by promoting healthy bacteria growth while inhibiting bad bacteria and other organisms in the gastrointestinal tract.Protein also helps protect against infections and illness caused by bacteria and viruses including E. coli and salmonella.
Fats :- For the first couple of years after baby is born, fats is very important for their development; and breast milk is chock full of fats.These are necessary for proper brain, retina, and nervous system development and for the absorption of certain vitamins. It is also their primary calorie source which helps with physical growth and feeling full.
Vitamins :- Between what is already present in breast milk and what you take in through your food and prenatal vitamins, your baby receives all the vitamins they need without the use of supplements. However, it is very important that you continue on your prenatal vitamins and maintain a healthy diet so your baby doesn’t suffer from a vitamin deficiency.
Carbohydrates :- Similar to proteins, carbohydrates – like the main one found in breast milk, lactose – help to regulate unhealthy bacteria in the stomach to improve vitamin absorption and fight disease.
Antibodies :- The majority of babies who are breastfed are sick much less often than those on formula. They suffer far fewer cases of meningitis, ear and respiratory tract infections, gut problems, and urinary tract infections.
Why? Well, it is thanks to not only the proteins and lactose that regulate bacteria growth in the gut but also due to the presence of antibodies found in breast milk.
Breast milk contains all five forms of antibodies (immunoglobins): IgG, IgA, IgM, IgD, and IgE, though IgA is found in the highest abundance. These help to create and strengthen baby’s immune system. These antibodies are particularly effective against colds, which will help them fight the cold quickly or even avoid it altogether.
It is also important to introduce a variety of safe and nutritious complementary foods at 6 months of age, while continuing to breastfeed until your child is two years old and beyond.
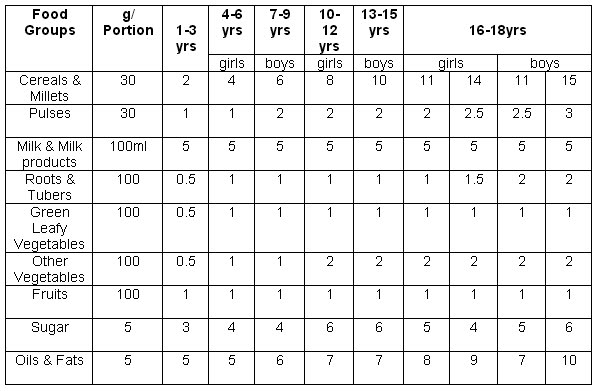
A Healthy Diet Chart For Children
A Healthy Diet Chart For Adults
Cereals:- Cereals are the greatest source of energy for humans. They are rich in complex carbohydrates (60-70%), that provide you almost 30% of total calories in a regular diet, and help to prevent cancer, constipation, colon disorders, and high blood sugar levels. They also enrich your overall health with abundant proteins, fats, lipids, minerals, vitamins, and enzymes. In cereals, around 95% of minerals are sulfates and phosphates of magnesium, potassium, and calcium. A good amount of phosphorous, called phytin, is present in cereals. Zinc, copper, and manganese are also present small quantities. But Rice is the poorest source of iron and calcium.
Cereals are enriched with niacin, iron, riboflavin, and thiamine and most cereals have abundant fiber contents, especially barley, oat, and wheat. Cereals also have soluble bran that aids in lowering blood cholesterol levels and keeping heart diseases at bay. Cereal consumption also means an intake of high amounts of protein. For infants, iron-fortified cereals are said to be the premium solid foods.
Main cereals:- Wheat, Rice, Brown Rice, Maize, Barley, Sorghum, Oats, Rye, Triticale, Fonio,Buckwheat, Quinoa etc.
Millets:- The millet has bright green leaves and small, round seeds. Millet is staple foods for both humans and animals. Millet are various types of. The most important millets are pearl millet, finger millet, proso millet and foxtail millet. All the seeds of millets are tiny in size and varied in colors of white, yellow, red or gray. Proso millet, also named common millet.
Even though millets are generally considered as a famine crop for the poor, they are nutritionally superior to the widely consumed polished white rice or white flour. Millet is a rich source of dietary fibres, vitamins, calcium, iron and magnesium. None of the millets are closely related to wheat and they don’t contain any gluten. It is gluten free and has low glyceamic index. This makes them appropriate foods for those with coeliac disease or having allergy or intolerance to wheat as well as people with high blood glucose concern.
Pulses are the edible seeds of plants. Pulses is variety of shapes, sizes and colors. Popular pulses include dry beans, dry broad beans, dry peas, chickpeas, cow peas, pigeon peas, lentils, Bambara beans, vetches, lupins and pulses nes.
Pulses high in protein, fibre, and various vitamins. But they are the major sources of protein in the diet. Pulses contain about 20 to 25 per cent protein by weight which is double the protein content of wheat and three times that of rice.
Milk is a highly nutritious liquid. It contains almost every single nutrient that your body needs. A huge variety of food products are made from buffalo and cow's milk, such as cheese, cream, butter, and yogurt.
One cup (240 ml) of whole cow’s milk with 3.25% fat provides:
Vitamin B12- Foods of animal origin are the only rich sources of this essential vitamin. B12 is very high in Milk.
Calcium- Milk is not only one of the best dietary sources of calcium, but the calcium found in milk is also easily absorbed.
Riboflavin- Dairy products are the biggest source of riboflavin, also known as vitamin B2.
Phosphorus- Dairy products are a good source of phosphorus, a mineral that plays an essential role in many biological processes.
Milk is an excellent source of high-quality protein and different fats. More than 50 different hormones are naturally present in milk, which are important for the development of health.
Fruits and vegetables should be an important part of your daily diet as they contain vitamins and minerals that can help keep you healthy. They can also help protect against some diseases.
Vitamins and Minerals:- Fruits and vegetables include vitamins A (beta-carotene), C and E, magnesium, zinc, phosphorous and folic acid. Folic acid may reduce blood levels of homocysteine, a substance that may be a risk factor for coronary heart disease.
Protection against diseases :- Fruits and vegetables contain phytochemicals, or plant chemicals. These biologically active substances can help to protect you from some diseases. A diet rich in vegetables and fruits can prevent some types of cancer, lower risk of eye and digestive problems, and have a positive effect upon blood sugar, which can help keep appetite in check. Eating non-starchy vegetables and fruits like apples, pears, and green leafy vegetables may even promote weight loss. Their low glycemic loads prevent blood sugar spikes that can increase hunger.
Types of Fruit
Fruits are usually eaten raw, although some varieties can be cooked. They come in a wide variety of colors, shapes and flavours. Common types of fruits that are readily available include:
Types of vegetables
Vegetables are available in many varieties and can be classified into biological groups or ‘families’, including:
Everybody likes to eat sugary foods, but very few think about how much sugar they are consuming.
Sugary foods and drinks tend to contain empty calories and usually in excess. Refined sugar has no vitamins, no minerals, no fiber, no protein and no other essential nutrients that are important for your health.
Avoid these foods, in order of importance:
Soft drinks :- Sugar-sweetened beverages are unhealthy. You should avoid these like the plague.
Fruit juices :- Fruit juices actually contain the same amount of sugar as soft drinks! Choose whole fruit instead of fruit juice.
Candies and sweets :- You should drastically limit your consumption of sweets.
Baked goods :- Cookies, cakes, etc. These tend to be very high in sugar and refined carbohydrates.
Fruits canned in syrup:- Choose fresh fruits instead.
Low-fat or diet foods :- Foods that have had the fat removed from them are often very high in sugar.
Drink water instead of soda or juices and don't add sugar to your coffee or tea.
Instead of sugar in recipes, you can try things like cinnamon, nutmeg, almond extract, vanilla, ginger or lemon.
Fats and Oils is an important part of a healthy diet. The term ‘fat’ and ‘oil’ are often used to mean the same thing. You need a small amount of fat in your diet for healthy functioning. Oils and fats supply calories and essential fats and help your body absorb fat-soluble vitamins such as A, D, E and K, and They help in keeping our joints running smooth, just like machines require oil to run smoothly. Fats also make foods feel and taste rich and satisfying. They signal the stomach that enough food has been eaten, and giving you the feeling of satiety that encourages you to stop eating before they overeat.
it's important to choose healthier unsaturated fats. Eating too much and the wrong kinds of fats, such as saturated and trans fats, may raise unhealthy LDL cholesterol and lower healthy HDL cholesterol. This imbalance can increase your risk of high blood pressure, hardening of the arteries (atherosclerosis), heart attack and stroke.
Fats can be classified into four groups. Each type of fat behaves differently inside the body. Saturated fats
Saturated fats contribute to the risk of cardiovascular diseases (such as heart disease and stroke), because they raise LDL blood cholesterol levels. These fats are commonly found in many discretionary foods and drinks (those to only have sometimes), such as takeaway (‘fast’) foods, and in commercial products such as biscuits and pastries.
Saturated fats are also found in some everyday, healthy foods such as dairy products and meats. It is recommended to select lower saturated fat options. For example, choose :- reduced-fat milk, yogurt and cheese, leaner cuts of meat or trim the fat off meat prior to cooking.
Mono-unsaturated and poly-unsaturated fats
Mono-unsaturated and poly-unsaturated fats both tend to lower LDL blood cholesterol when they replace saturated fats in the diet. Poly-unsaturated fats have a slightly greater impact than mono-unsaturated fats. Poly-unsaturated fats are divided into two categories, omega-3, omega-6.
Where possible, replace foods and drinks high in saturated fat with either monounsaturated or polyunsaturated alternatives. For example :- replace butter with olive oil or margarine, replace potato chips or chocolate with plain nuts as a healthier snack alternative, replace fried fast food with a sandwich or wrap made with lean meat and salad.
Trans fats
Trans fats tend to behave like saturated fats in the body, as they raise LDL blood cholesterol levels and increase the risk of cardiovascular diseases (such as heart disease and stroke). Unlike saturated fats, they tend to also lower HDL cholesterol.
Trans fats are rare in nature – they are only created in the stomach of cows and sheep. Because of this, trans fats are naturally found in small amounts in milk, cheese, beef and lamb. Trans fats are also created during the manufacture of some baked products such as pies, pastries, cakes, biscuits and buns.
Sodium — often simply referred to as salt — is found in nearly everything you eat and drink.
Salt is also used as a flavoring agent in food at home and restaurants. But sodium has been linked to high blood pressure, which causes damage to your blood vessels and arteries when chronically elevated. In turn, this increases your risk of heart disease, stroke, heart failure and kidney disease. Therefore are established guidelines for limiting sodium intake.
Keeping your salt intake to less than 5h per day helps prevent hypertension and reduces the risk of heart disease and stroke in the adult population.
Limiting the amount of salt and high-sodium condiments (soy sauce and fish sauce) when cooking and preparing foods helps reduce salt intake.
A Healthy Diet Chart For Adults
Combination of different foods and Important Elements in healthy diet
Energy is required in adequate amounts to perform daily physiological activities and to stay energised. Energy is mostly derived from carbohydrates and its healthy sources include whole Cereals and millets. Fresh whole fruits, vegetables and Pulses also provide with a lot of energy.1. Cereals and Millets
Cereals and Millets are the major important grains in the human diet, and are important sources of nutrients.Cereals:- Cereals are the greatest source of energy for humans. They are rich in complex carbohydrates (60-70%), that provide you almost 30% of total calories in a regular diet, and help to prevent cancer, constipation, colon disorders, and high blood sugar levels. They also enrich your overall health with abundant proteins, fats, lipids, minerals, vitamins, and enzymes. In cereals, around 95% of minerals are sulfates and phosphates of magnesium, potassium, and calcium. A good amount of phosphorous, called phytin, is present in cereals. Zinc, copper, and manganese are also present small quantities. But Rice is the poorest source of iron and calcium.
Cereals are enriched with niacin, iron, riboflavin, and thiamine and most cereals have abundant fiber contents, especially barley, oat, and wheat. Cereals also have soluble bran that aids in lowering blood cholesterol levels and keeping heart diseases at bay. Cereal consumption also means an intake of high amounts of protein. For infants, iron-fortified cereals are said to be the premium solid foods.
Main cereals:- Wheat, Rice, Brown Rice, Maize, Barley, Sorghum, Oats, Rye, Triticale, Fonio,Buckwheat, Quinoa etc.
Millets:- The millet has bright green leaves and small, round seeds. Millet is staple foods for both humans and animals. Millet are various types of. The most important millets are pearl millet, finger millet, proso millet and foxtail millet. All the seeds of millets are tiny in size and varied in colors of white, yellow, red or gray. Proso millet, also named common millet.
Even though millets are generally considered as a famine crop for the poor, they are nutritionally superior to the widely consumed polished white rice or white flour. Millet is a rich source of dietary fibres, vitamins, calcium, iron and magnesium. None of the millets are closely related to wheat and they don’t contain any gluten. It is gluten free and has low glyceamic index. This makes them appropriate foods for those with coeliac disease or having allergy or intolerance to wheat as well as people with high blood glucose concern.
2. Pulses
Pulses high in protein, fibre, and various vitamins. But they are the major sources of protein in the diet. Pulses contain about 20 to 25 per cent protein by weight which is double the protein content of wheat and three times that of rice.
3. Milk & Milk products
One cup (240 ml) of whole cow’s milk with 3.25% fat provides:
- Calories: 149
- Water: 88%
- Protein: 7.7 grams
- Carbs: 11.7 grams
- Sugar: 12.3 grams
- Fiber: 0 grams
- Fat: 8 grams
Vitamin B12- Foods of animal origin are the only rich sources of this essential vitamin. B12 is very high in Milk.
Calcium- Milk is not only one of the best dietary sources of calcium, but the calcium found in milk is also easily absorbed.
Riboflavin- Dairy products are the biggest source of riboflavin, also known as vitamin B2.
Phosphorus- Dairy products are a good source of phosphorus, a mineral that plays an essential role in many biological processes.
Milk is an excellent source of high-quality protein and different fats. More than 50 different hormones are naturally present in milk, which are important for the development of health.
4. Fruits and vegetables
Vitamins and Minerals:- Fruits and vegetables include vitamins A (beta-carotene), C and E, magnesium, zinc, phosphorous and folic acid. Folic acid may reduce blood levels of homocysteine, a substance that may be a risk factor for coronary heart disease.
Protection against diseases :- Fruits and vegetables contain phytochemicals, or plant chemicals. These biologically active substances can help to protect you from some diseases. A diet rich in vegetables and fruits can prevent some types of cancer, lower risk of eye and digestive problems, and have a positive effect upon blood sugar, which can help keep appetite in check. Eating non-starchy vegetables and fruits like apples, pears, and green leafy vegetables may even promote weight loss. Their low glycemic loads prevent blood sugar spikes that can increase hunger.
Types of Fruit
Fruits are usually eaten raw, although some varieties can be cooked. They come in a wide variety of colors, shapes and flavours. Common types of fruits that are readily available include:
- Apples and pears
- Tomatoes and avocados.
- Citrus – oranges, grapefruits, mandarins and limes
- Tropical and exotic – bananas and mangoes
- Berries – strawberries, raspberries, blueberries, kiwifruit and passionfruit
- Melons – watermelons, rockmelons and honeydew melons
- Stone fruit – nectarines, apricots, peaches and plums
Types of vegetables
Vegetables are available in many varieties and can be classified into biological groups or ‘families’, including:
- Leafy green – lettuce, spinach and silverbeet
- Root – potato, sweet potato and yam
- Allium – onion, garlic and shallot.
- Cruciferous – cabbage, cauliflower, Brussels sprouts and broccoli
- Marrow – pumpkin, cucumber and zucchini
- Edible plant stem – celery and asparagus
5. Limit intake of sugars
Sugary foods and drinks tend to contain empty calories and usually in excess. Refined sugar has no vitamins, no minerals, no fiber, no protein and no other essential nutrients that are important for your health.
Avoid these foods, in order of importance:
Soft drinks :- Sugar-sweetened beverages are unhealthy. You should avoid these like the plague.
Fruit juices :- Fruit juices actually contain the same amount of sugar as soft drinks! Choose whole fruit instead of fruit juice.
Candies and sweets :- You should drastically limit your consumption of sweets.
Baked goods :- Cookies, cakes, etc. These tend to be very high in sugar and refined carbohydrates.
Fruits canned in syrup:- Choose fresh fruits instead.
Low-fat or diet foods :- Foods that have had the fat removed from them are often very high in sugar.
Drink water instead of soda or juices and don't add sugar to your coffee or tea.
Instead of sugar in recipes, you can try things like cinnamon, nutmeg, almond extract, vanilla, ginger or lemon.
Other Important Elements Of A Healthy Diet
1. Fats and Oils
it's important to choose healthier unsaturated fats. Eating too much and the wrong kinds of fats, such as saturated and trans fats, may raise unhealthy LDL cholesterol and lower healthy HDL cholesterol. This imbalance can increase your risk of high blood pressure, hardening of the arteries (atherosclerosis), heart attack and stroke.
Fats can be classified into four groups. Each type of fat behaves differently inside the body. Saturated fats
Saturated fats contribute to the risk of cardiovascular diseases (such as heart disease and stroke), because they raise LDL blood cholesterol levels. These fats are commonly found in many discretionary foods and drinks (those to only have sometimes), such as takeaway (‘fast’) foods, and in commercial products such as biscuits and pastries.
Saturated fats are also found in some everyday, healthy foods such as dairy products and meats. It is recommended to select lower saturated fat options. For example, choose :- reduced-fat milk, yogurt and cheese, leaner cuts of meat or trim the fat off meat prior to cooking.
Mono-unsaturated and poly-unsaturated fats
Mono-unsaturated and poly-unsaturated fats both tend to lower LDL blood cholesterol when they replace saturated fats in the diet. Poly-unsaturated fats have a slightly greater impact than mono-unsaturated fats. Poly-unsaturated fats are divided into two categories, omega-3, omega-6.
Where possible, replace foods and drinks high in saturated fat with either monounsaturated or polyunsaturated alternatives. For example :- replace butter with olive oil or margarine, replace potato chips or chocolate with plain nuts as a healthier snack alternative, replace fried fast food with a sandwich or wrap made with lean meat and salad.
Trans fats
Trans fats tend to behave like saturated fats in the body, as they raise LDL blood cholesterol levels and increase the risk of cardiovascular diseases (such as heart disease and stroke). Unlike saturated fats, they tend to also lower HDL cholesterol.
Trans fats are rare in nature – they are only created in the stomach of cows and sheep. Because of this, trans fats are naturally found in small amounts in milk, cheese, beef and lamb. Trans fats are also created during the manufacture of some baked products such as pies, pastries, cakes, biscuits and buns.
6. Sodium & Salt
Salt is also used as a flavoring agent in food at home and restaurants. But sodium has been linked to high blood pressure, which causes damage to your blood vessels and arteries when chronically elevated. In turn, this increases your risk of heart disease, stroke, heart failure and kidney disease. Therefore are established guidelines for limiting sodium intake.
Keeping your salt intake to less than 5h per day helps prevent hypertension and reduces the risk of heart disease and stroke in the adult population.
Limiting the amount of salt and high-sodium condiments (soy sauce and fish sauce) when cooking and preparing foods helps reduce salt intake.












0 Comments